Gigabit Switch vs. Fast Ethernet Switch: what is the difference?

Industrial Gigabit Switch or Industrial Fast Ethernet Switch?
Ethernet is a network communication protocol designed to connect industrial networking devices, industrial switches and industrial routers. Ethernet function in wired or wireless networks, including wide area networks (WAN) and local area networks (LAN). The demand for higher bandwidth for high-quality transmission and uninterrupted video streaming has led to the development of Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. What is the difference between switches? Which one is more suitable for a given project? Here are the characteristics of the Industrial Fast Ethernet Switch and the Industrial Gigabit Switch, and then we compare the two types with each other to help you better choose a device.
Industrial Fast Ethernet Switch
Fast Ethernet is known as an updated version of the original Ethernet that further increases speed - it has increased Ethernet transfer rates from 10 megabits per second (10 Mbps) to 100 megabits per second (100 Mbps). Meanwhile, the Industrial Fast Ethernet Switch also supports the 10/100 protocol, which is capable of operating at 100 megabits per second. Fast Ethernet transmission is at least 10 times faster than standard Ethernet and proves useful in maintaining compliant connections to high-speed servers, supporting multiple IP video cameras and IoT, and seamlessly handling complex networks controlling multiple bandwidth-intensive software packets at the same time.
It is designed for 100 Base T networks and is also compatible with 10 Base T networks, allowing users to enjoy faster Ethernet speeds (using compatible industrial switches) without having to completely upgrade their network systems. Typically equipped with RJ45 ports, Fast Ethernet Switches operate over Cat5 cables to connect PCs, servers, routers, etc. Many Industrial Fast Ethernet Switches are also equipped with high-speed uplink ports, where copper/fiber modules can be used to connect fiber or UTP cabling supporting speeds of 1 Gbps or more. However, the maximum length and capacity of UTP cabling is 100 meters, and throughput can be limited. Fiber optic transmission allows for longer distances and higher throughput over UTP cabling, enabling Fast Ethernet network devices to deliver their full potential.
Presented below available from Us Industrial Fast Ethernet Switch IES318-1F
Industrial Gigabit Switch
Gigabit Ethernet is ten times faster than its predecessor, Fast Ethernet. It is designed to meet the high-speed needs of ISPs. The Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switch, a higher version of the Fast Ethernet switch, supports transmission speeds of up to 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps) (1000 Mbps), where the Industrial Fast Ethernet Switch can transmit data packets at 10 megabits per second. It is also backward compatible with the older 10/100 standard.
The IEEE 802.3ab standard defined the applicability of Gigabit Ethernet to 1000 Base T networks and allowed the use of existing UTP cabling. Typically built with multiple RJ45 interfaces and/or SFP slots, a gigabit industrial network switch works well with twisted-pair copper cables (specifically, cat5e and cat6 cables compliant with the 1000BASE-T cabling standard), as well as SFP optical transceivers that work with the appropriate types of interconnect cables. It is common for some Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switches to also have several 10G SFP+ ports for connecting upwards of a 10GB switch with higher speeds. Gigabit Ethernet can meet increasingly complex networking requirements, such as connecting multiple high-bandwidth devices and broadband Internet connections for video streaming. Gigabit Ethernet applications include industrial gigabit switches that can manage data transfer between multiple IP security cameras and network devices, as well as transfer other high-quality signals between servers and high-resolution monitors and devices.
Shown below available from Us Industrial Gigabit Switch IES206-2GS
Differences of Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet
In addition to a markedly increased transfer rate and better performance, the Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switch differs from the Industrial Fast Ethernet Switch in the following aspects:
- Feature sets: The Industrial Gigabit Switch is typically built with the latest network management features, allowing network administrators to assign QoS and security policies to specific applications. These advanced features help guarantee service level agreements and enhance security. Industrial Fast Ethernet Switches with similar management and security features often require a higher price to reduce the price difference compared to Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switches.
- Power Standard: The original PoE technology provides 12.94 watts for wireless access points and other IP-enabled devices. This does not meet the power requirements of newer equipment. The latest Industrial Gigabit Switches support the improved PoE+ standard, which provides 30 watts of power. Yet vendors are not updating their existing Industrial Fast Ethernet Switches with the new power standard.
- Power consumption: In addition to providing higher bandwidth and more reliable management, Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switches are also more energy efficient than Industrial Fast Ethernet Switches. Enterprises can reduce energy consumption by deploying an Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switch.
- Future development: Compared to Industrial Fast Ethernet Switches, Industrial Gigabit Switches with great flexibility prepares your local network for the coming convergence or the next technology upgrade.
Comparison of Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet
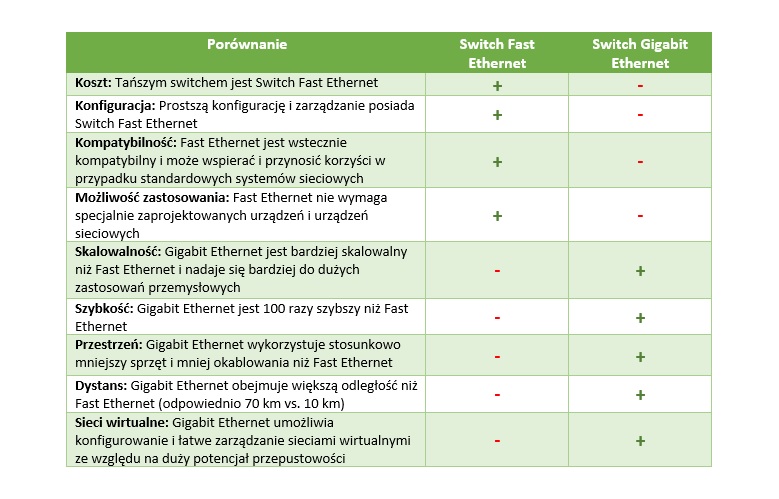
Still wondering between these two industrial Switches?
Before choosing between a Industrial Gigabit Ethernet Switch and a Industrial Fast Ethernet Switch for your network, consider your current deployment, budget, transmission speed requirements and future needs. Conteel Electronics is available to assist you with the selection of industrial equipment for individual telephone technical support before the sale. For contact information, see Contact.
..








































































