What is a BACnet router and what role does it play in building automation systems?

What is a BACnet router and what role does it play in building automation systems?
The most common question is: “What is a BACnet router?” Simply put, a BACnet router is a key component of modern building automation systems (BMS – Building Management System), responsible for connecting, segmenting and optimizing communication between devices operating in the BACnet protocol. With increasingly complex HVAC installations, lighting automation, access control and energy monitoring, a proper understanding of the BACnet router’s role is fundamental for designers, integrators and system administrators.
BACnet (Building Automation and Control Networks) is an open communication standard designed specifically for building automation. A BACnet router is not a typical network device—its function goes far beyond simple data transmission. It is a component that provides scalability, stability and security of communication throughout the entire BMS.
What is BACnet?
BACnet is an international, open communication protocol (ISO 16484-5), developed for building and industrial automation systems. It enables data exchange between devices from different manufacturers, such as HVAC controllers, VAV controllers, air handling units, energy meters, lighting systems or operator panels.
A key feature of BACnet is its object-oriented data model. Each device exposes information as objects (e.g., temperature, fan status, CO₂ level) that can be read and written by other devices on the network. This makes system integration consistent, clear and predictable.
BACnet can operate on different physical and transport layers, including:
- BACnet MS/TP (RS-485),
- BACnet IP (Ethernet),
- BACnet Ethernet,
- BACnet over ARCNET (less common).
This variety of transmission media is exactly why a BACnet router becomes an essential element in larger installations.
Is BACnet the same as Ethernet?
This is one of the most frequently asked questions and also a common source of confusion. BACnet is not the same as Ethernet, although it can use it.
Ethernet is a physical and data-link layer technology—it defines how frames are transmitted in a network. BACnet, on the other hand, is an application protocol that defines which data is exchanged and how it is interpreted by automation devices.
In practice, this means that:
- BACnet IP runs over Ethernet and uses the IP/UDP protocol stack,
- BACnet MS/TP runs on the RS-485 bus and has nothing to do with Ethernet,
- both BACnet variants can coexist within one system, but they require the right communication infrastructure.
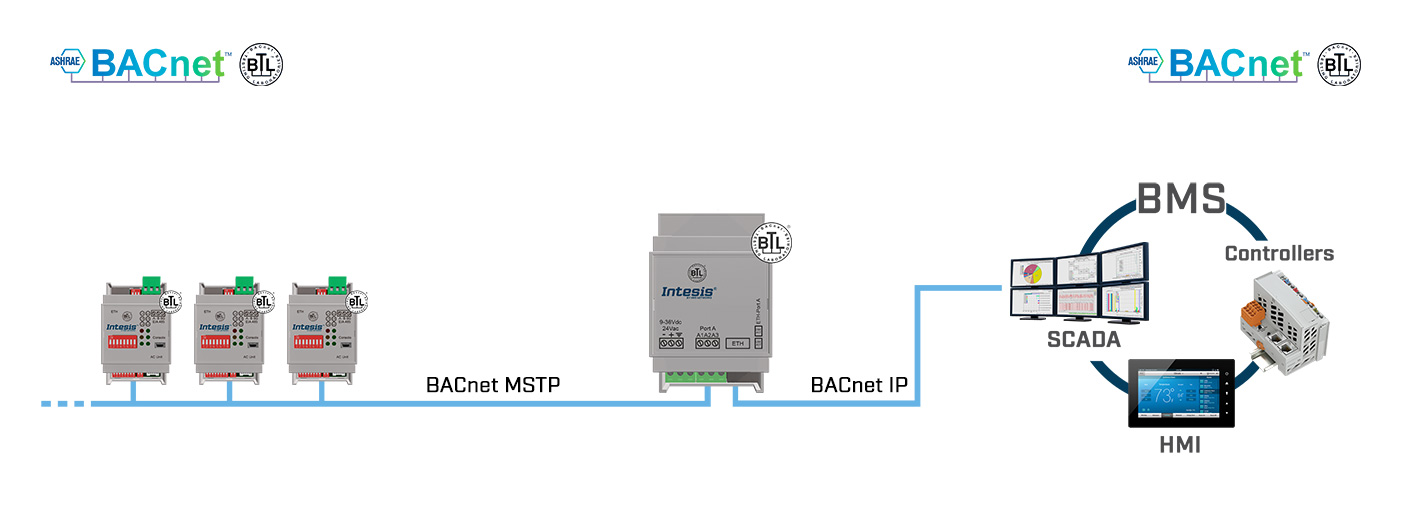
And this is where a BACnet router comes in, enabling communication between different BACnet networks (e.g., MS/TP - IP), while maintaining full protocol compliance, addressing and routing mechanisms.
What is the difference between a router and a gateway in BACnet?
Distinguishing between a BACnet router and a BACnet gateway is crucial from the perspective of BMS architecture.
BACnet Router
A BACnet router connects different BACnet networks but does not change the protocol. This means:
- BACnet remains BACnet on both sides,
- the structure of objects, services and addressing is preserved,
- devices see each other as native components within one logical BACnet network.
Typical BACnet router applications include:
- connecting multiple BACnet MS/TP segments to a supervisory BACnet IP network,
- separating network traffic and reducing broadcasts,
- scaling systems in large buildings or campus environments.
BACnet Gateway
A BACnet gateway is used for protocol conversion, for example:
- Modbus RTU - BACnet IP,
- KNX - BACnet,
- DALI - BACnet.
In this case, data is mapped between different communication models. A gateway is not a router—it does not connect BACnet networks; instead, it translates data between different standards.
In summary:
- BACnet router = routing within BACnet,
- BACnet gateway = BACnet-to-other-protocol conversion.
This distinction is very important when selecting devices, licensing BMS software, and troubleshooting communication issues.
Why is a BACnet router critical in modern BMS installations?
As the number of devices in HVAC installations and building automation systems grows, the need increases for:
- network segmentation,
- reduction of broadcast traffic,
- improved communication stability and determinism,
- easier address management.
A BACnet router enables a logical division of the system into subnets, which:
- increases reliability,
- simplifies commissioning and service,
- allows system expansion without the risk of overloading the bus.
In addition, many BACnet routers offer features such as:
- broadcast filtering,
- galvanic isolation of ports,
- MS/TP network diagnostics,
- support for APDU segmentation,
- IP communication redundancy.
BACnet Router - summary of key features
A BACnet router is a fundamental component of scalable and professional building automation systems. It should not be confused with a standard Ethernet router or a protocol gateway. Its role is to intelligently connect BACnet network segments, ensure correct communication, and maintain high performance of the entire BMS.
Understanding the differences between BACnet, Ethernet, a router and a gateway helps avoid costly design mistakes and significantly simplifies the integration of devices from various manufacturers into one coherent automation system.
If you want to select a BACnet router suitable for your HVAC installation or BMS, it is worth consulting our advisor, who will consider both the network topology and future system expansion so that the BACnet router meets all your requirements.










































































