Network Management Technology: Layer 3 Switch and Router

Among many networking products, industrial switches play an important role in building high-performance networks, and their technical development is equally rapid and remarkable. The slogan "Industrial Layer 3 Switch" has become more popular in the industrial automation industry. In large and medium-sized networks, there are many networks with gigabit layer 3 switches as the core. With the rapid development of enterprise networks, campus networks and broadband networks, industrial switch layer 3 has become a new market growth point. Its application has penetrated from the backbone layer and aggregation layer of the initial network center to the access layer at the network edge.

Development of switching technology
The combination of computer technology and communications technology has promoted the rapid development of computer LAN. From the advent of the Aloha network in the late 1960s to the advent of the Gigabit Ethernet Switch in the late 1990s. It went through development from simplex to duplex, splitting to switching, low speed to high speed, simple to complex, expensive to popular, and the leap from Layer 2 switching to multilayer switching.
Layer 2 switching, or Industrial Layer 2 Switching

In the early days of LAN networking, it was mainly limited to host connection, file sharing and printing. These requirements could be met by sharing 10Mbps bandwidth among multiple users. As the scale of the network increases, the previous network system is no longer competent, because in a LAN, the earliest device that connects networks is the hub, which is a layer one (physical) device. In this network based on the CSMA / CD physical layer protocol, there is often a conflict of user data, this leads to retransmission of data, which greatly reduces the efficiency of transmission. At this time, the second layer (data link layer) hardware bridge was adopted, which can improve the network segment and reduce the conflict domain to optimize LAN performance. However, the bridge is a high-level protocol transparent device (above the third layer), which cannot effectively prevent starfish storm, so it is necessary to use a router. Industrial routers play a key role in connecting subnets, controlling security and mitigating broadcast storms, but complex algorithms and low data throughput make them a network bottleneck. To solve the above problems, the industry has improved the bridge and produced a LAN switch to replace the hub to improve network performance. The LAN switch is a Layer 2 network device. During operation, it constantly collects and establishes its own MAC address table and refreshes it regularly. Its introduction makes each network station have its own exclusive bandwidth, eliminates unnecessary conflict detection and error retransmission, improves transmission efficiency. Since user data transmission is point-to-point, it is invisible to other nodes. However, Industrial Layer 2 Ethernet Switch also has its weaknesses, including the inability to effectively solve the problems of transmission storm, heterogeneous network interconnection and security control, so VLAN (virtual local area network) technology is introduced on the switch.
Layer 3 switching, or Industrial Layer 3 Switch
Industrial Layer 2 Switch operates at the second layer of the OSI reference model-data link layer. Its main functions include physical addressing, network topological structure, error control, frame sequencing, flow control and so on. In order to improve the switch's performance, a Layer 3 industrial switch was introduced. It retained all the Layer 2 features and has many new options, such as VLAN support, aggregation link support and even firewall function. In summary, the Industrial Layer 3 Switch adds routing function in protocol-based VLAN partitioning. The Layer 3 Switch is a key intranet application. It organically and intelligently combines the advantages of a Layer 2 switch and Layer 3 routers into a flexible solution that can deliver line-rate performance at all levels. This integrated structure also introduces a policy management attribute that not only connects the second layer and third layer, but also provides traffic prioritization processing, security access mechanism and other functions. The Industrial Ethernet Switch Layer 3 is divided into three parts: the interface layer, the switching layer and the routing layer. The interface layer covers all important LAN interfaces, such as 10 / 100Mbps Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, FDDI, ATM, etc. The switching layer integrates various LAN interfaces, supplemented by policy management, and provides link aggregation, VLAN and labeling mechanisms. The routing layer provides major LAN routing protocols, including IP, IPX and AppleTalk, etc. It also provides Layer 3 forwarding technology for traditional routing or directly through policy management. The combination of policy management and administrative management enables network administrators to customize networks to meet specific enterprise needs.
Industrial Layer 3 Switches adopt programmable and expandable ASIC chip technology that can provide rich functions such as:
From industrial router to industrial layer switch
In the past, most of the data in the network followed the "80 / 20" rule, that is, only about 20% of the data packets in the network communicate with the central server or other parts of the enterprise network through the backbone router, while 80% of the network traffic was still concentrated in various departmental subnetworks. Now, however, the situation has fundamentally changed, so the "20 / 80" rule has emerged. To cope with the growing data traffic, networks with shared media have been replaced by switching networks. This change has a direct impact on the traditional router originally used for network segmentation. Since most data traffic crosses an IP subnet, the router has effectively become a network transmission limiter. The main function of the traditional router is to implement routing and network connection, that is, to obtain information about the subnet topology and network characteristics of each physical line in a certain way. An important task is to obtain the best path to each subnet through a specific routing algorithm and establish a proper routing table to forward each IP packet to its destination, as well as dealing with different link protocols. When IP packets pass through each router, they have to go through software processing links, such as queuing, protocol processing and addressing routing, which increases latency. At the same time, the router adopts a shared bus model, and the total bandwidth is limited. When the number of users increases, the access speed of each user decreases. Industrial routers are paying more attention to supporting different media types and transmission speeds. Today, data buffering and conversion capabilities are more important than line-rate throughput and low latency. Although router performance has also improved recently, about 1mpps, the cost of using it is also surprisingly high.
Compared to routing technology, switching technology has the advantage of fast speed. When the scale of the network is large, a router with high speed and capacity is very necessary. On the other hand, since most modern communication networks use fiber optic technology, the main bottleneck of the data network is the node router. Today's Layer 3 switching, routing switching or other terms are the result of this idea. Although Layer 3 switches were originally designed for LAN networks and uses a destination IP address for switching this technology has now also been used in WAN. Layer 3 switching is playing an increasingly important role in current network design. It does not need to distribute broadcast packets, but directly uses dynamically determined MAC addresses for communication, such as IP address and ARP and so on. It has the functions of multi-channel broadcasting and routing between virtual networks based on IP and IPX protocols and so on. Efficient implementation of this function mainly depends on application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). The instructions processed by traditional routing software have been changed to the embedded instructions of the ASIC chip, which speeds up packet forwarding and filtering, and provides linear routing and great quality of service at high speed.
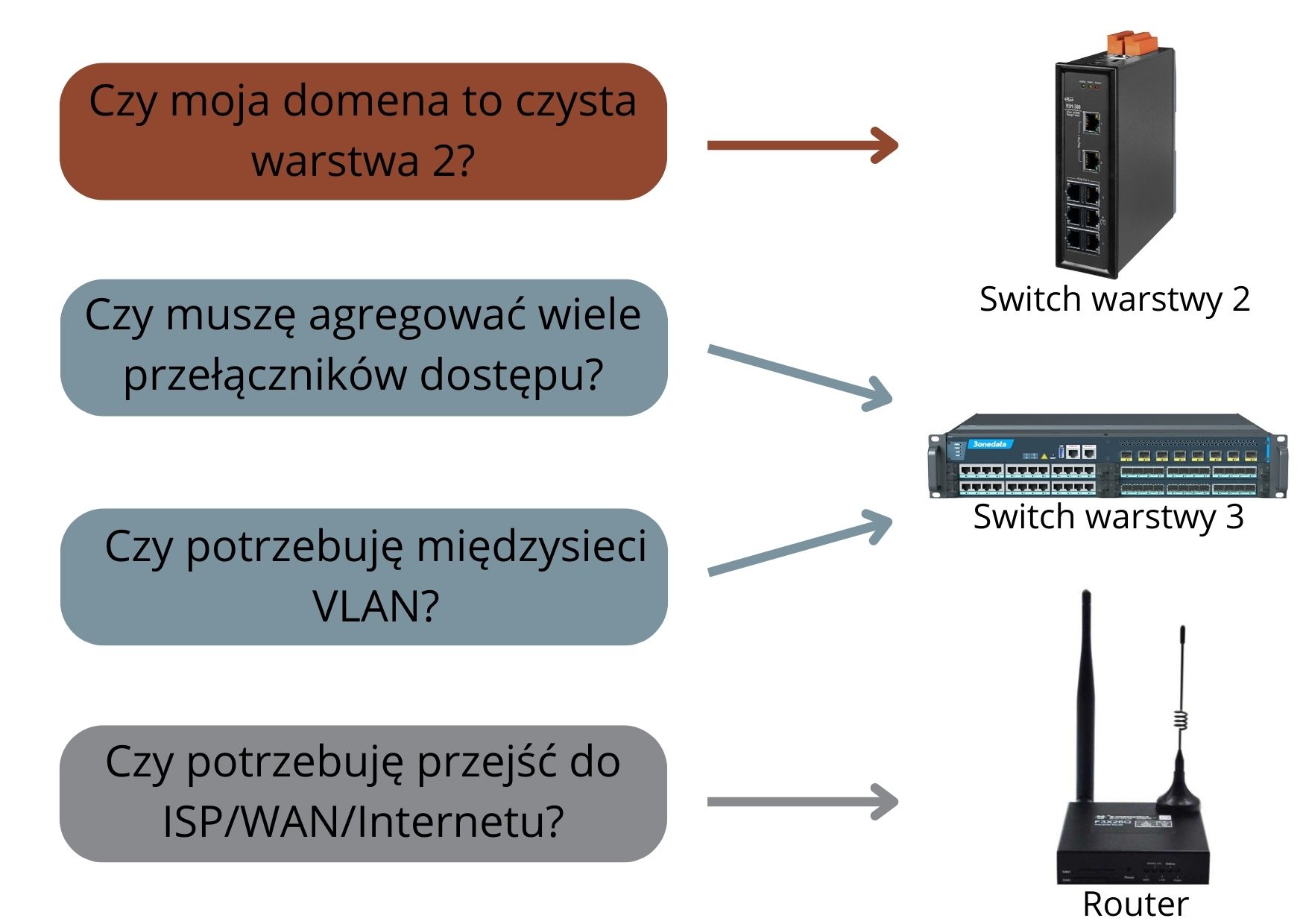
In order to choose the right and best industrial device, here is an image that answers the question of when to use a Layer 2 Switch, when to use a Layer 3 Switch, and when to use an Industrial Router