What is OPC UA and why interest in it is growing

What is OPC UA and why its use will grow?
OPC (Open Platform Communications) and OPC UA (Unified Architecture) are standards that facilitate the exchange of data between programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), servers, clients and other machines to ensure interconnection and information flow.
This kind of interconnection and communication is obviously essential in a manufacturing plant, as there are many different types of equipment, devices and machines that measure process parameters, produce data or record it.
Historically, classic OPC consisted of three main separate protocols, namely OPC Historical Data Access (OPC HDA), OPC Data Access (OPC DA), OPC Alarms and Events (OPC A & E) and other protocols that have been adopted by many in the manufacturing industry for their connectivity needs. Classic OPC, however, is platform-dependent and relies on Windows-based technologies.
OPC UA is the main successor to classic OPC. One of its main advantages is that it is platform-independent, so it can be easily connected to Windows, Linux, Mac, Android and other platforms, which is an important thing for the manufacturing industry, where machines and systems are often run on different platforms. OPC UA also combines all the separate protocols into a single specification, so there is simplification. Other key advantages are that OPC UA can be easily deployed, data exchange is secure, it can accommodate legacy systems as well as existing infrastructure, and it also allows for scalability, i.e., scaling up the system.
The ability to accommodate legacy systems satisfies plants and factories that do not necessarily have the budget to purchase new IT equipment and infrastructure, which is another important positive in the context of OPC UA.
OPC UA has thus been adopted in the process quality control, oil and gas, food and beverage, waste management and pharmaceutical industries.

The role of OPC UA in the manufacturing industry
The manufacturing industry has many complex operational and communication requirements. Machines, sensors, server, client, applications and various devices, produce numerous outputs and data points. This data often needs to be exchanged between machines and equipment, and ultimately analyzed to improve production rates, reduce waste, increase profits, and identify new value chains and business models.
Additionally, in many cases there is often a geographic context to consider. Consider a scenario in which a food company produces meat, cheese and other dairy products at different plants. Each of these plants has its own systems, equipment and production lines. The company has decided that it needs to focus on reducing waste and increasing production rates, while maintaining compliance with safety standards.
To achieve these goals, individual plants must send large amounts of data to remote servers, and these servers would need to be able to make sense of the various data from the many sources they receive. In addition, the company has developed a reporting application that runs on Linux, generating trends based on data from the plants. It has also developed another application that runs on Windows and analyzes the trends identified by the reporting application. This application then suggests new settings for machines based on the trends to achieve the company's goals of reducing losses and increasing production rates. The main challenges in this scenario are, of course, data sharing, interpretation and delivery.
The OPC UA solution would be the ideal answer to this dilemma. A company could set up OPC UA servers that would be able to receive data from different machines and devices in different locations and translate it into a format that a reporting application could further use.
Furthermore, the servers would also be able to communicate between the reporting application running on Linux and the application running on Windows. Finally, the OPC UA servers would be able to send the final, customized settings for machines back to the plants and the machines there, in specific formats.
The company could then achieve its goals in a cost-effective and efficient manner.
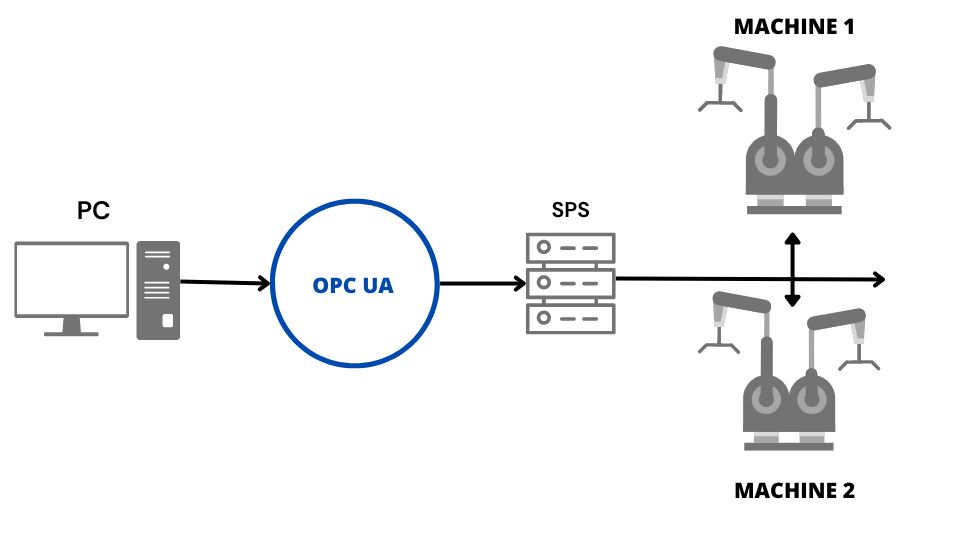
The main role of OPC UA in the manufacturing industry, as shown in the example above, is to facilitate industrial communication and break down traditional barriers in it.
Main reasons why OPC UA will be increasingly used in the industrial industry:
- Provides smart manufacturing
- Contributes to reducing complex communication between equipment and machines, thereby improving overall plant efficiency
- Can easily adapt to legacy systems, new machines and product lines
- It is cross-platform
- This is not a proprietary format
- Can receive and interpret multiple data points from different sources
The obvious fact is that OPC UA was created to become a foundation, regularly updated with other technologies and new standards, if only mobile technology or JSON.
The manufacturing sector is a highly competitive space and companies operating in this sphere must consistently produce high-quality products to maintain a competitive edge. Therefore, many companies in this sector are investing in various innovative technologies to stay ahead.
OPC UA addresses many of the key challenges facing the industrial sector, and ultimately the implementation of the OPC UA standard results in less waste, higher profits and reduced operating costs.
It is therefore well positioned and capable of meeting the demands of the ever-changing industrial sector.
Now that you know what OPC UA is and the benefits it brings, see our industrial converters based on this very protocol.










































































