What is LoRaWAN and what is it used for?

What is the LORAWAN protocol?
The term "LoRaWAN" refers to the Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) protocol and system network architecture. The physical layer of LoRaWAN is based on LoRa modulation, which provides long-distance communication between smart devices, gateways and end users. The range of LoRaWAN can be up to 15 km, which is much longer than Wi-Fi; besides, the LoRaWAN protocol is more economical to deploy compared to cellular IOT technologies (in remote areas). In addition, LoRaWAN meets the requirements of the Internet of Things (IoT), such as two-way communication, end-to-end security, mobility, and provision of location-based services.
How does LoRaWAN work?
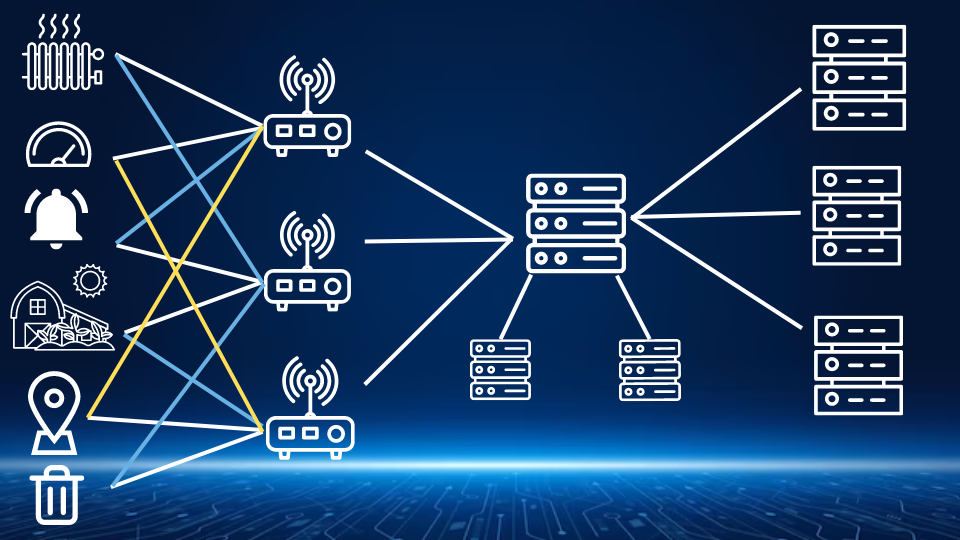
LoRaWAN works by sending data packets on a common radio frequency, allowing devices to communicate with each other. Data exchange between machines is enabled by a network of gateways that act as collectors, allowing LoRaWAN devices to send and receive data on a given radio frequency. These gateways are connected to the Internet, ensuring that data is sent from the devices to the LoRaWAN server, which is then accessed by the end user. On the other hand, the transmission of data packets is carried out using LoRa modulation, which ensures the transmission of information over a wide range of frequencies and over long distances, using low power consumption.
What is a LoRaWAN gateway
A LoRaWAN gateway is a device used to provide a fixed LoRaWAN signal, similar to a cellular network, that allows LoRaWAN devices to communicate with the server and application their owner is using. Put simply, it acts as a bridge between the physical world and the virtual world. The gateway receives data from LoRaWAN devices and then passes it to the network server, which stores it and distributes it to applications as needed. The LoRaWAN gateway also supports communication in the other direction, from cloud-based applications to physical devices.

LoRa, LoRaWAN and LPWAN
LoRaWAN and LPWAN are low-power broadband network technologies that are used to support the Internet of Things (IoT). They provide many benefits for IoT applications, such as long range, low power consumption and cost savings. Although LoRaWAN and LPWAN share many common features, each technology offers different performance metrics in terms of latency, throughput, distance covered, etc.
LoRa
LoRa (Long Range Radio) is an advanced low-power physical layer technology used for long-distance wireless data exchange. The technology relies on spread spectrum modulation techniques to reduce power consumption and increase transmission range, allowing data to be transmitted over long distances. LoRa is best suited for applications requiring low data rates and long range, i.e. remote asset tracking and machine-to-machine (M2M) communications.
LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a wireless network protocol designed to provide secure, reliable and cost-effective communications for IoT applications. The protocol is based on LoRa physical layer technology and uses a network topology with a "star" structure with gateways connecting end devices to a central network server.
LPWAN
LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) is a general term referring to wireless network technologies that are designed to be energy efficient and can provide long-distance data transmission. The technology focuses on low data rate applications like sensor networks. LPWAN does not always have to be used together with LoRa. The solution can be based on one of the technologies, LoRaWAN is one example, other technologies include Sigfox, NB-IoT, Weightless, etc.
Benefits of LoRaWAN
Long range and coverage: Its range, which can reach up to 15 kilometers and is unrivaled by other communication protocols,
High throughput: A single LoRa gateway can connect thousands of IoT end devices,
Low cost of ownership: LoRaWAN devices are highly energy efficient: moreover, various open-source licensed infrastructures, such as gateways, are being developed, further reducing the costs associated with such networks,
Low power consumption: LoRa technology delivers extremely low power consumption via radio communications, making it ideal for devices that need to survive a decade or more on a single power supply.
LoRaWAN delimitations
Despite its many advantages, LoRaWAN has some limitations that should be considered before it is implemented.
First, LoRaWAN does not offer universal coverage. Unlike cellular networks, LoRaWAN is often deployed in areas where no network has coverage. Fortunately, it is possible to extend LoRaWAN coverage to an area of interest through carrier support, as well as deploy and operate your own business network.
Secondly, applications requiring mobile devices need coverage in areas where the devices will roam. This may require roaming agreements with nearby network operators. It is likely that the devices will roam in an area larger than the network the user is interested in, and cooperation with neighboring networks can be very useful in this case.
Third, LoRaWAN has a limited data rate, which is less than 50 kbps. This makes it unsuitable for applications requiring higher data rates, such as video or audio streaming.
LoRaWAN classes
In LoRaWAN there are 3 classes of devices with different capabilities and different energy consumption profiles: class A, B and C.
Class A is the most economical. Devices of this class are battery-powered for several years, this is made possible by the fact that the device happens to be active only for a short time, at the time of data transmission according to a programmed schedule and for an additional time immediately after this transmission to allow the network to communicate with another device. The rest of the time, the device is in sleep, power-saving mode.
Class B is an extension of the Class A communication model, allowing devices to schedule connection transmissions during designated ping slots. This allows applications to send control messages during designated windows without waiting for an outgoing message from the device. Class B devices must have time synchronization with the network before they can receive messages sent by the gateway. Once a Class B device is properly time-synchronized, it enters message retrieval mode during ping slots to ensure that it can receive any messages sent from the network. As a result, Class B offers much lower latency than Class A; it is a mode with lower battery consumption compared to continuously powering the device as in Class C.
Class C, on the other hand, is a mode designed for end devices that allows communication with devices from the gateway at almost any time. It requires more power than its Class A or B counterparts, but offers the lowest latency when sending data from applications to end devices.
LoRaWAN use cases
LoRaWAN can be successfully used in transportation, smart buildings, agriculture, medicine, oil and gas and many other areas of the economy.
Logistics and transportation
With LoRaWAN-based IoT solutions, supply chain and logistics companies are successfully tracking high-value assets, including those in transit. Vehicles, goods and other supporting materials are efficiently tracked across geographic regions and in harsh environments, thanks to the technology's remarkable range, low power consumption and GPS-free location. IoT solutions allow vehicles to be monitored using LoRaWAN connectivity, so they can stay on the road longer, reduce fuel consumption, increase safety, provide insight into vehicle maintenance issues and improve overall operational efficiency.

Intelligent cities
Smart cities require real-time access to all areas of urban life. To achieve this, smart cities typically use wide-area wireless networks, with the goal of enabling connectivity between a vast network of multiple IoT devices generating data from sensors and smart meters. Wireless technology LoRaWAN is the best IoT solution for smart city applications. Using IoT technology with various smart devices to visualize and analyze complex data in real time, cities can dynamically respond by optimizing the use and allocation of local resources. Cities can integrate IoT into their structure, aiming to automate tasks, monitor and manage equipment, and perform preventive maintenance to reduce operating costs. Cities around the world can effectively optimize utility and personnel efficiency by integrating city services such as:
Street lighting
Water level and flood management
Smart public transportation
Air quality control
Smart buildings
Motion detection
Smart water measurement
Monitoring of fire, flood, CO/CO2 levels.
Intelligent agriculture
The concept of using IoT technology based on LoRaWAN applied to smart farming practices is gaining more and more momentum, driven by the ease of visualizing, analyzing and making more informed decisions about crops, livestock, equipment, infrastructure, environment and all other aspects that need to be constantly monitored and managed to increase crop yields and improve farm productivity. Agricultural IoT sensors, thanks to their small size, can determine many parameters that make it easier to understand environmental issues. IoT sensors can be deployed to collect sunlight exposure data, which can be used to make more accurate crop placement decisions and help determine if solar integration is a viable option for the farm.

Intelligent healthcare
Low power consumption, low cost and consistent performance make LoRaWAN networks ideal for key applications in the smart healthcare sector. LoRaWAN-based Internet of Things solutions are able to help continuously monitor patients or high-risk systems, ensuring that medical health and safety are not compromised. A LoRaWAN-based IoT system can be used to continuously and reliably monitor the vital signs of hospital patients, the elderly, athletes or others who require continuous real-time insight into their vital signs.
Public safety
There is a growing demand for comprehensive safety and security solutions. IoT-enabled public safety systems provide emergency responders with cutting-edge technology that can reduce vulnerability and improve people's lives. Individual IoT devices for everyday use, such as ID cards, are equipped with LoRaWAN technology, the built-in panic button when pressed sends an instant SOS signal with the user's location information to the relevant services.
If you already know what, is LoRaWAN, what are its advantages and applications get acquainted with our offer of industrial converters based just on this protocol.
.