M-bus industrial protocol - the most important information

Nowadays, when technology and automation strive to automate as many things and systems as possible, the natural path is to introduce as many remote data retrieval and reading solutions as possible. With the wide availability of protocols, connecting some systems is quite a challenge. However, most are based on communications using the most popular communication protocols. One of them is M-Bus. It is one of the most recognized protocols in Europe.

How was the M-Bus protocol developed?"
It was created in cooperation between the University of Padeborn and the German company Texas Instruments. Work on the introduction of the protocol began as early as 1990. The main goal of the developers was to create an inexpensive system for remote reading of readings of meters or battery-powered measuring devices. Meters that can communicate thanks to the M-Bus protocol include water, gas, heat and electricity meters. Since the introduction of M-Bus over the years, it has been constantly updated and eagerly used by leaders in the BMS industry, and the standard that was finally given to M-Bus is EN13757.
Requirements for M-Bus
Because of its application in a specific environment, the M-Bus protocol must meet certain requirements. One of them is the reading of data from a large number of devices far apart from each other. This requirement was closely related to the very nature of the installation of meters, which are located at considerable distances from each other in the building. Sometimes it is necessary to read data even at a distance of several kilometers. Communication via M-Bus protocol is also very well protected against the occurrence of errors during transmission. It is also characteristic of the M-Bus protocol that data is not read very often in real time. The transmission speed ranges from 300 to 9600 baud.
M-Bus hardware converter
For some specific communications using the M-Bus protocol, it will also be necessary to use a converter is so, for example, for meter communication. With M-Bus, meters communicate through a special physical interface (36V), which means the necessary use of a converter from M-Bus protocol to RS232, RS485, RS422 or Ethernet. There are many solutions available on the market one of the most popular in Europe are converters from Adfweb, which are characterized by high robustness and easy configuration.
M-Bus topology
A network using M-Bus can be implemented using one of three topologies. Depending on the needs of the project, we can use:
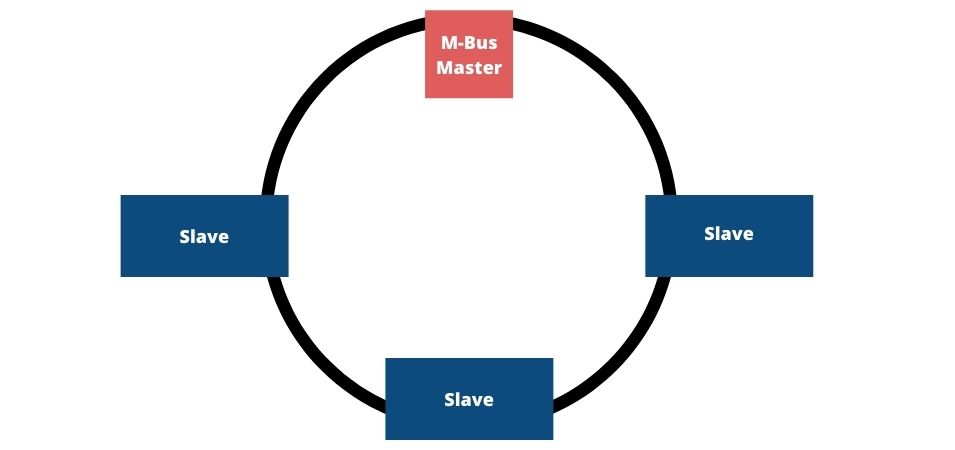
Ring topology (Ring topology) - characterized by each unit being connected to another in a so-called "Daisy chain".
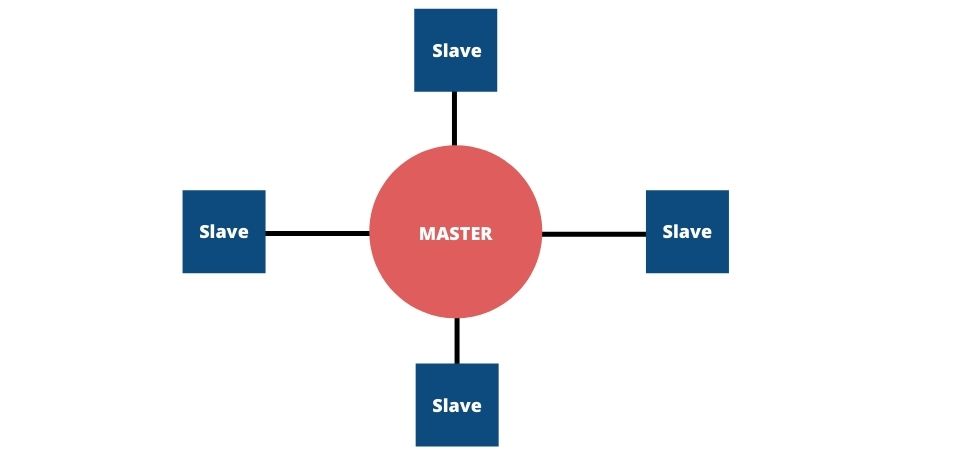
Star topology (Star topology)-a topology that is characterized by an individual transmission line for the Master with each Slave
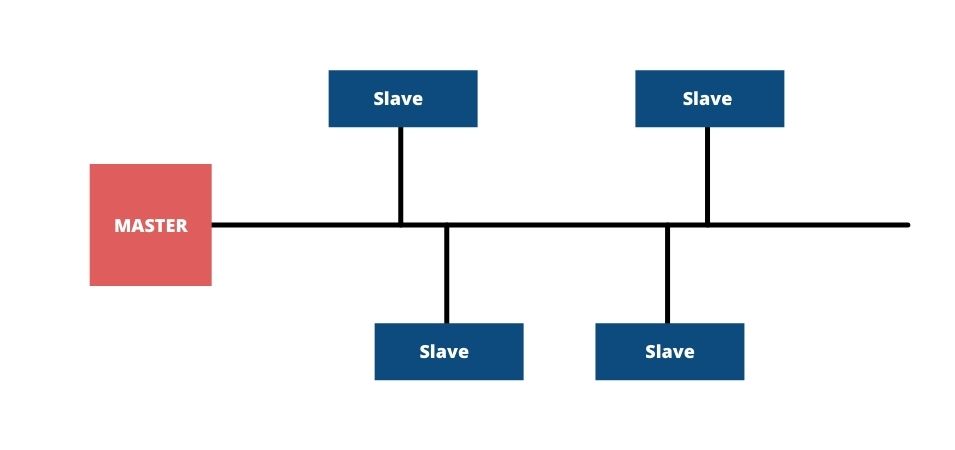
Bus topology (Bus topology)- is characterized by less use of network cabling, so that in the event of failure, the various parts are not dependent on each other. It is one of the most widely used solutions.
M-Bus application
As previously mentioned modules with M-Bus protocol are used to read and transmit energy consumption data information from heat meters, gas meters, water meters, sensors or actuators from various manufacturers. The Meter-Bus module is the most widely used solution in the field of building control as an efficient system designed to read aggregate utility consumption data.










































































