Differences between 2 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi

Differences between 2G and 5G Wi-Fi
The Wi-Fi router in your home or office uses radio frequencies to transmit the Internet to various devices. Generally speaking, there are two most common radio frequencies, i.e. 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, which are used when setting up a wireless local area network WLAN. However, most people don't know which radio frequency will best suit their network requirements and usually end up choosing the wrong device.
Characteristics of the 2.4 GHz band
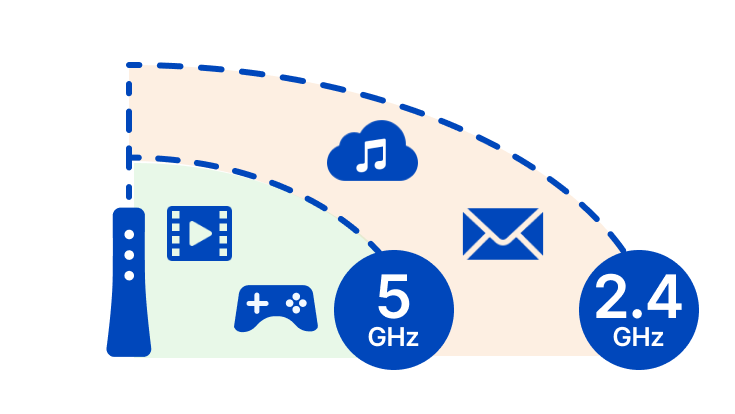
2.4 GHz is the most common radio frequency that is used by most electrical devices. It is relatively slower than 5G Wi-Fi, but can be used to cover a fairly large area. Basically, if you want to use Wi-Fi over a larger area and have too many devices that use the 2.4GHz radio frequency, choosing the 2G band will be the right choice. It will provide you with optimal speed and all your electronic devices can be easily connected to Wi-Fi. The only downside of using the 2.4GHz band is that it is more susceptible to interference, making internet speeds slower.
Frequency characteristics of 5 GHz
The 5 GHz band is quite fast and can provide a maximum speed of up to 2 GB per second. However, a Wi-Fi router operating on the 5 GHz radio frequency will only cover a small area. This means it will be ideal if you plan to place your electronic devices near the router and won't be moving them around. The 5GHz band is also an ideal choice for users who plan to perform advanced online activities such as live streaming, video conferencing, gaming, etc. By getting fast internet speeds, you won't have to worry about unexpected interruptions while using the network.
Differences between 2G and 5G Wi-Fi signals
Can you use both frequencies on the same router?
Because both radio frequencies cater to different network requirements, many people also want to know, is it possible to set up 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz on the same router at the same time? The answer is yes! Today you can buy dual-band routers that will allow you to transmit both frequencies simultaneously.
When you set up such routers, you will see two different network SSIDs (with the same, identical name) on your devices. The only difference between the two networks will be that they transmit the Internet using different frequencies. This means that you will be able to choose the right frequency according to your current network requirements.
For example, if you're sitting in the same room with a Wi-Fi router, you can choose the 5 GHz frequency and enjoy fast and uninterrupted Internet speeds. However, if you are in another room of the building, you can easily switch to the 2.4 GHz frequency and enjoy the Internet at optimal speed.
Some of the modern Wi-Fi routers even have the function to automatically switch between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, making it easy for the user to get the most optimal speed depending on the current environment.
When it comes to choosing the right radio frequency for your Wi-Fi installation, you must first analyze your requirements and then make the right decision. However, if you want to use both frequencies, you can opt for dual-band Wi-Fi routers. They will help you switch between the two radio frequencies depending on the situation, and you will be able to enjoy an uninterrupted Internet connection.
If you already know what Wi-Fi frequency your network requires, check out our range of industrial Wi-Fi routers









































































